

<rss version="0.91"> <channel> <item> <title>Kde zachytávat výjimky</title> <link>http://php.vrana.cz/kde-zachytavat-vyjimky.php</link> </item> <item> <title>Kde zachytáváte výjimky?</title> <link>http://php.vrana.cz/kde-zachytavate-vyjimky.php</link> </item> <item> <title>Jak je to s těmi chybami?</title> <link>http://php.vrana.cz/jak-je-to-s-temi-chybami.php</link> </item> </channel> </rss>
$rss = simplexml_load_file($filename);
echo $rss["version"] . "\n";
foreach ($rss->channel->item as $item) {
echo $item->title . "\n";
}
-> to access inside elements
foreach to iterate through elements
$elements[3] to access element by its order
$element["attribute"] to access attributes
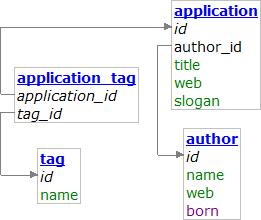
$db = new NotORM($pdo);
foreach ($db->application() as $application) { // get all applications
echo $application["title"] . "\n"; // print application title
echo $application->author["name"] . "\n"; // get name of the application author
}
-> to access tables
foreach to iterate through rows
$table[3] to access a row by ID
$row["column"] to access a value
Easy and efficient access to database data
Uses PDO (tested with MySQL, SQLite, PostgreSQL, MS SQL, Oracle)
Free even for commercial use (Apache license)
$db = new NotORM($pdo[, $structure[, $cache]])$table = $db->$tableName([$where[, $parameters[, ...]]])$tableName$table->where($where[, $parameters[, ...]])WHERE$table->order($columns)ORDER BY, can be expression ("columm DESC, id DESC")$table->select($columns)"col, MD5(col) AS hash")$table->limit($limit[, $offset])LIMIT and OFFSET$table->group($functions[, $having])"COUNT(*), MAX(published)")count($table)(string) $tableforeach ($table as $id => $row)$row = $db->$tableName[$id]$id from table $tableName$row = $table[$id]$id from the result$row = $table->fetch()$data = $row[$column]$column$row2 = $row->$tableName$table2 = $row->$tableName([$where[, $parameters[, ...]]])(string) $rowRepetitive calls of where, order and select are possible – it will append values to the previous calls (where by AND). These methods plus limit provide a fluent interface so $table->where()->order()->limit() is possible (in any order). All methods are lazy – the query is not executed until necessary.
$row["author_id"] gets the numerical value of column, $row->author gets row representing the author from the table of authors.
$row->$tableName() builds "SELECT * FROM $tableName WHERE {$myTable}_id = $row[$primary]". The returned object can be customized as usual table results (with order, limit, ...) and then executed. All results are lazy and execute only a single query for each set of rows.
| Single query | Constant number | Multiple queries |
 |
 |
 |
$db->table("id", $id)
$structure = new NotORM_Structure_Convention(
$primary = 'id',
$foreign = '%s_id',
$table = '%s'
);
NotORM_Structure interface
NotORM_Structure_Discovery class (slow)
$id = $db->$tableName()->insert($array)$tableName and return the auto increment value$id = $db->$tableName($array)$db->$tableName()->insert($array)$affected = $table->update($array)$affected = $table->delete()$affected = $row->update($array)$affected = $row->update()$affected = $row->delete()$table->freeze()Available in separate branch
$array parameter holds column names in keys and data in values. Values are automatically quoted, SQL literals can be passed as objects of class NotORM_Literal, for example:Stores only the information about used columns, no data
tmpfs
Memory storage engine
$db->product("available", true)
->where("category_id", $db->category("active", true))
-- one query in most databases SELECT * FROM product WHERE available = 1 AND category_id IN ( SELECT id FROM category WHERE active = 1 ) -- two queries in MySQL for performance reasons
JOIN